sknano.generators.GrapheneGenerator¶
-
class
sknano.generators.GrapheneGenerator(*args, *, autogen=True, **kwargs)[source][source]¶ N-layer graphene generator class.Changed in version 0.3.11:
GrapheneGeneratoris now a sub-class of theConventionalCellGrapheneGeneratorclass to maintain backwards compatibility and also includes 2 new classmethods:from_primitive_cellandfrom_conventional_cell.Parameters: armchair_edge_length : float, optional
Length of armchair edge in nanometers
New in version 0.3.10.
zigzag_edge_length : float, optional
Length of zigzag edge in nanometers
New in version 0.3.10.
length : float, optional
Length of armchair edge in nanometers
Deprecated since version 0.3.10: Use armchair_edge_length instead
width : float, optional
Width of graphene sheet in nanometers
Deprecated since version 0.3.10: Use zigzag_edge_length instead
edge : {‘AC’, ‘armchair’, ‘ZZ’, ‘zigzag’}, optional
ArmChair or ZigZag edge along the length of the sheet.
Deprecated since version 0.3.10: No longer used!
basis : {
list}, optionalList of
strs of element symbols or atomic number of the two atom basis (default: [‘C’, ‘C’])New in version 0.3.10.
element1, element2 : {str, int}, optional
Element symbol or atomic number of basis
Atom1 and 2Deprecated since version 0.3.10: Use
basisinsteadbond : float, optional
bond length between nearest-neighbor atoms in Angstroms.
nlayers : int, optional
Number of graphene layers.
layer_spacing : float, optional
Distance between layers in Angstroms.
stacking_order : {‘AA’, ‘AB’}, optional
Stacking order of graphene layers
autogen : bool, optional
automatically generate unit cell and full structure
verbose : bool, optional
verbose output
Notes
The
GrapheneGeneratorclass and its subclasses generate graphene with either an armchair or zigzag edge using a 4-atom conventional unit cell. If you want to generate graphene as an unrolled nanotube, see theUnrolledSWNTGeneratorclass.See also
Examples
Start an interactive python or ipython session, then import the
GrapheneGeneratorclass.>>> from sknano.generators import GrapheneGenerator
Now generate a 20 nm AC x 1 nm ZZ graphene nano-ribbon.
>>> ACG = GrapheneGenerator(armchair_edge_length=20, zigzag_edge_length=1)
Save structure data in xyz format:
>>> ACG.save()
The rendered structure look like:
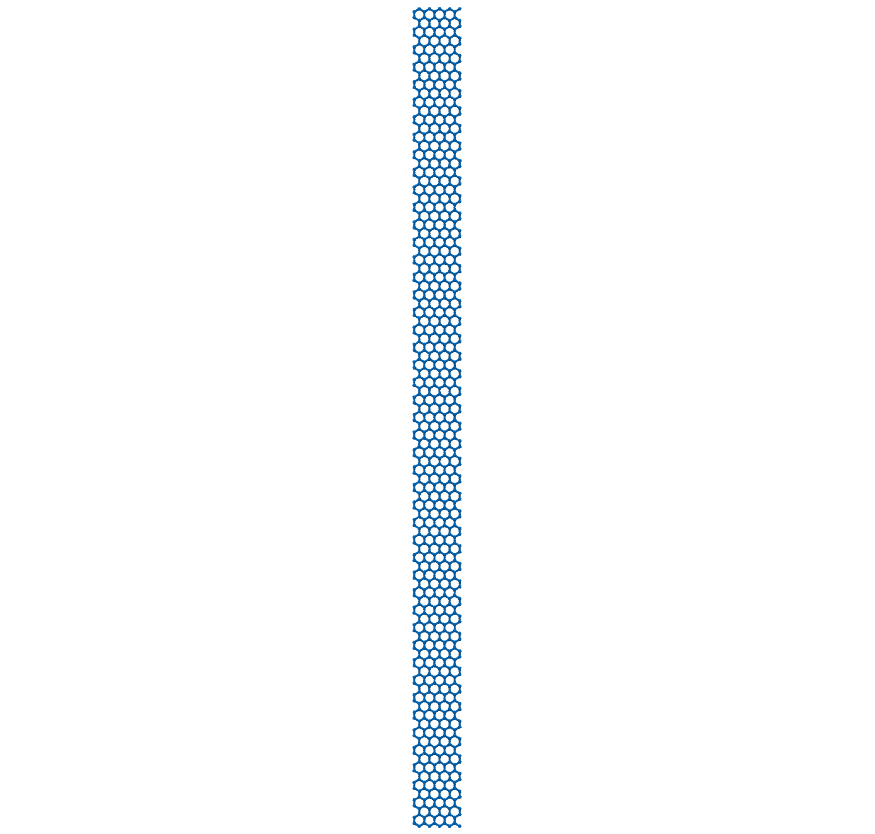
Now let’s generate a 20 nm ZZ x 1 nm AC graphene nano-ribbon.
>>> ZZG = GrapheneGenerator(armchair_edge_length=20, zigzag_edge_length=1) >>> ZZG.save()
The rendered structure looks like:
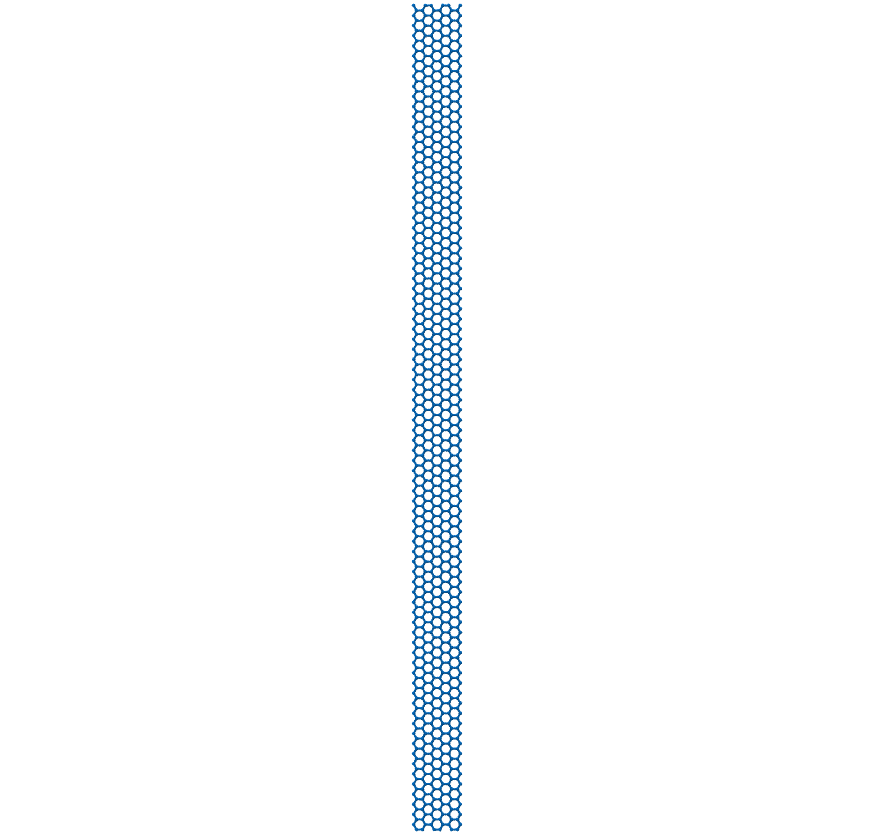
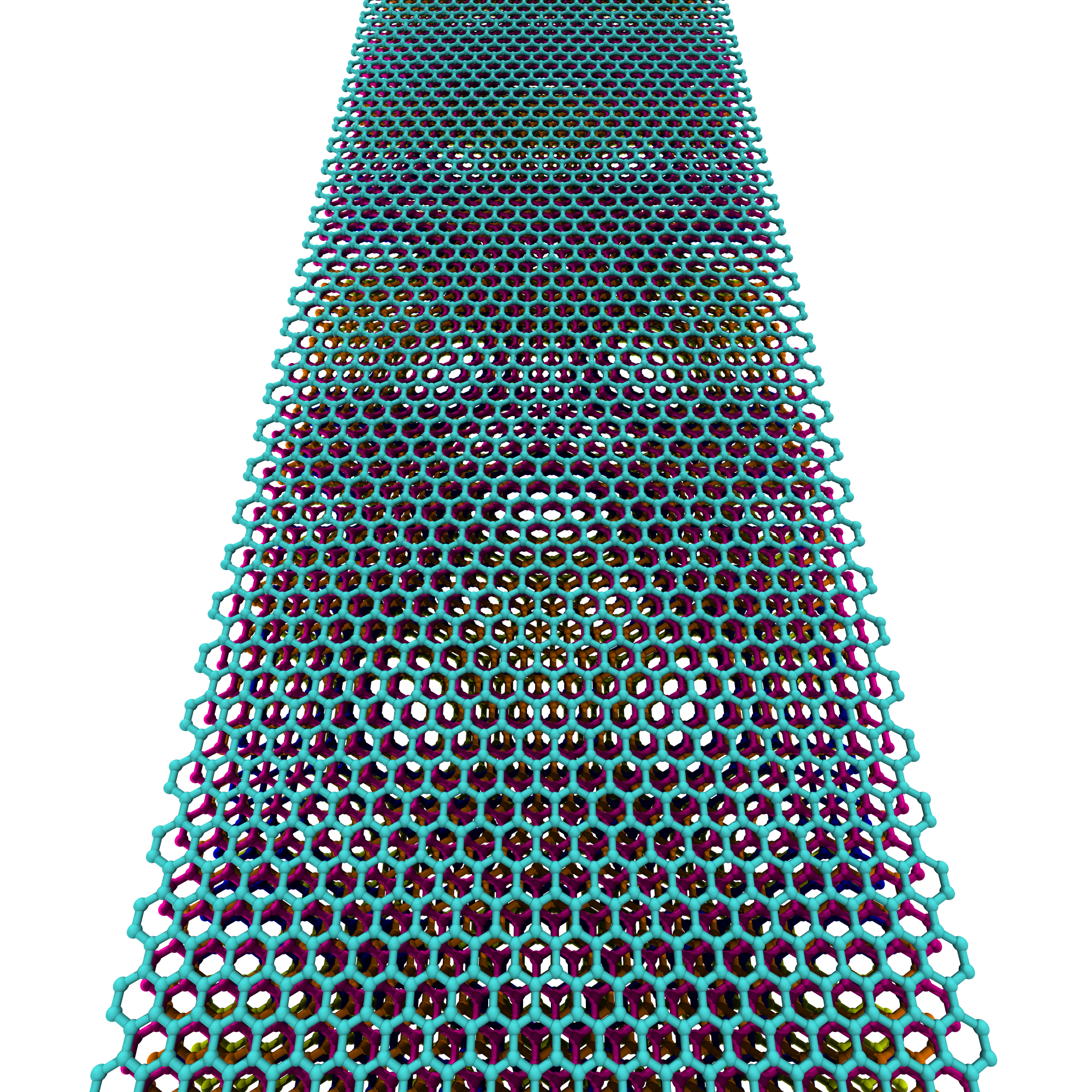
Now generate 25 nm AC x 5 nm ZZ, 5 layer, AB-stacked graphene.
>>> ACG_5layers = GrapheneGenerator(armchair_edge_length=25, ... zigzag_edge_length=5, ... nlayers=5) >>> ACG_5layers.save()
The rendered structure looks like:
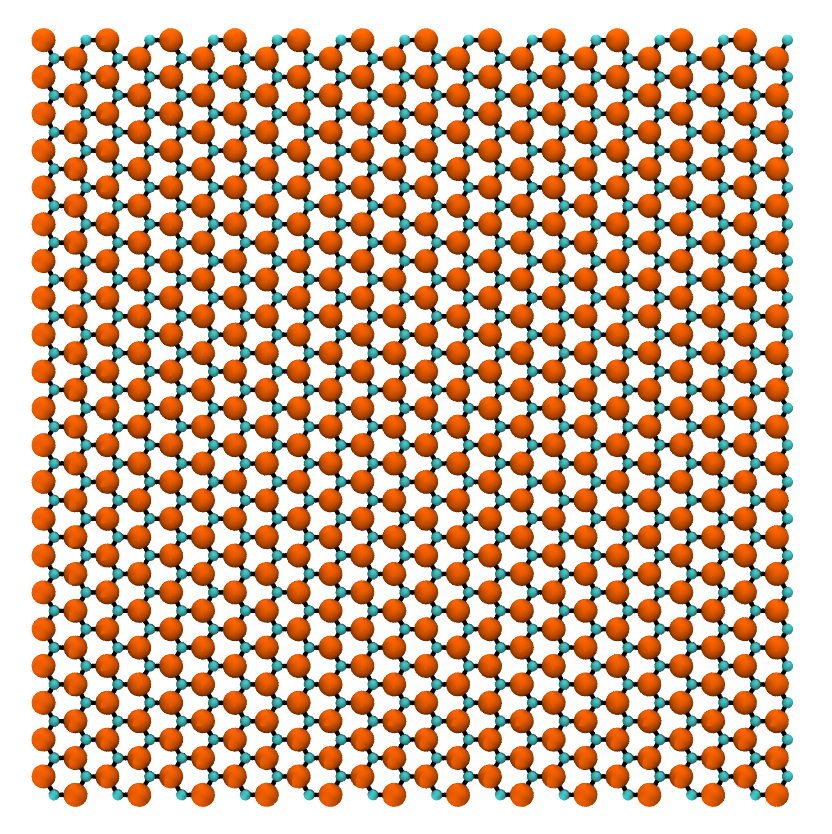
Now generate single layer, 10 nm x 10 nm sheet of BN Graphene.
>>> BN_graphene = GrapheneGenerator(armchair_edge_length=10, ... zigzag_edge_length=10, ... basis=['B', 'N']) >>> BN_graphene.save()
The rendered structure looks like:
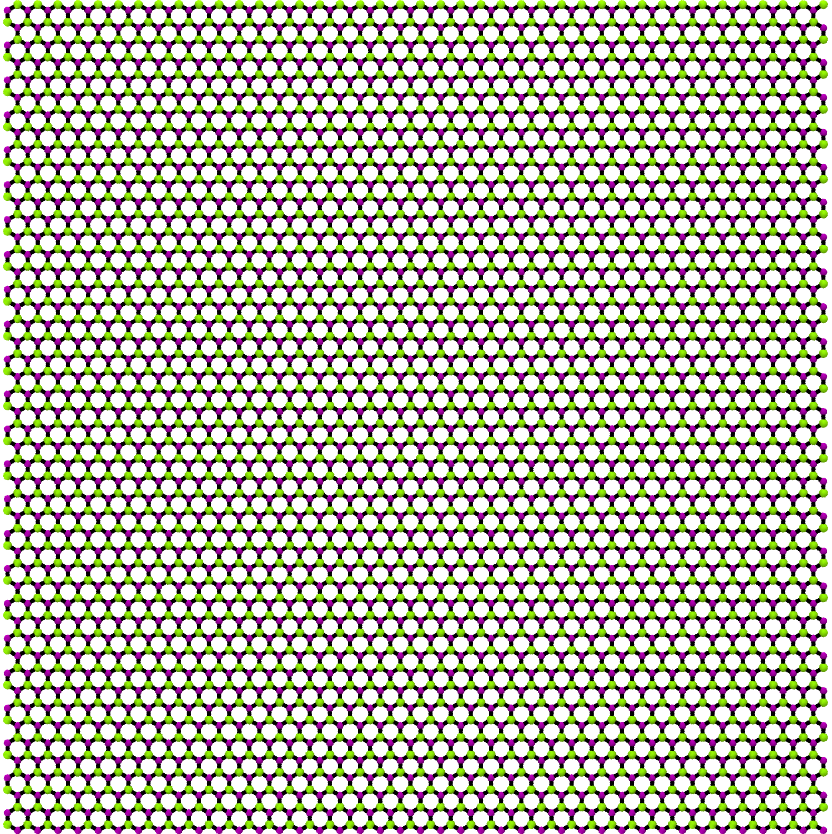
Now, just because we can, generate a 5 nm x 5 nm sheet of Uranium-Einsteinium Graphene.
>>> UEs_graphene = GrapheneGenerator(armchair_edge_length=5, ... zigzag_edge_length=5, ... basis=['U', 'Es']) >>> UEs_graphene.save()
The rendered structure looks like:
Attributes
NNumber of graphene unit cells. NatomsTotal number of atoms. Natoms_per_layerNumber of atoms per layer. Natoms_per_unit_cellNumber of atoms per unit cell. areaTotal area of graphene supercell. atomsStructure StructureAtoms.basisNanoStructureBasebasis atoms.crystal_cellStructure CrystalCell.element1Basis element 1 element2Basis element 2 fmtstrFormat string. latticeStructure Crystal3DLattice.n1n2r1r2scaling_matrixCrystalCell.scaling_matrix.structurePointer to self. structure_dataAlias for BaseStructureMixin.structure.unit_cellStructure UnitCell.vdw_distancevan der Waals distance. vdw_radiusvan der Waals radius Methods
clear()Clear list of BaseStructureMixin.atoms.from_conventional_cell(**kwargs)from_primitive_cell(**kwargs)generate()Generate the full structure coordinates. generate_fname([armchair_edge_length, ...])make_supercell(scaling_matrix[, wrap_coords])Make supercell. read_data(*args, **kwargs)read_dump(*args, **kwargs)read_xyz(*args, **kwargs)rotate(**kwargs)Rotate crystal cell lattice, basis, and unit cell. save([fname])Save structure data. todict()transform_lattice(scaling_matrix[, ...])translate(t[, fix_anchor_points])Translate crystal cell basis. write_data(**kwargs)write_dump(**kwargs)write_xyz(**kwargs)